The study of science aims to better understand how the natural world works, by observations and/or experimentation. Scientists collect information to test new ideas or to disprove old ones. Studying science can also help satisfy curiosity! Much of a scientist’s work these days is devoted to finding more efficient and ‘cleaner’ ways for society to run, such as renewable energy, agriculture and pollution management. Scientists usually work in research institutions or for private corporations but all have a goal of producing new understanding, products or technologies that contribute to society.
Biology is the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, origins, evolution and ecology. There are many sub-disciplines of biology that can be studied and can lead to a wide variety of careers in areas such as health care, medicine, vaccine development, management of natural environments (marine, freshwater etc.) forensics, genetics (including counselling) and microbiology (bacteria/viruses).
Chemistry is the study of the science of matter, atoms, molecules and their reactions. Chemists are the people who work on transforming everyday materials into amazing new products. Chemists work in a wide range of careers including medicine development, monitoring ozone levels, agriculture, making new textiles, forensics, food chemistry, most large industries, chemical engineering and materials science.
Psychology is the scientific study of the human mind and of the influence that the brain has on our behaviour. The structure and functions of the brain are an integral part of this study, as research is highlighting ways in which our brain influences our learning, memory, interactions with others, communication, sleep, development and mental health. Careers in psychology include counselling, welfare, police/defence force, forensic psychologists, sports psychologist, clinical psychologist and devising programs to test, modify and improve behaviour.
Physics is the study of matter, its energy and motion through space and time. Physics aims to understand how the universe behaves. Physicists help develop new technologies and studying physics can lead to careers in astronomy, sound engineering, weather forecasting, mechanical engineering, renewable energy management, radar use and development, and in becoming an aircraft pilot.
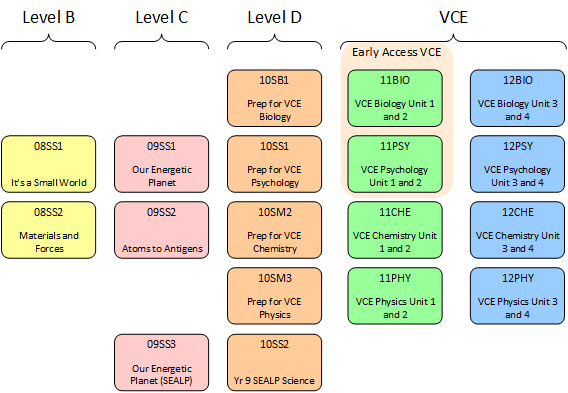
Ideas for Science pathways - Remember each unit is 5 periods per week for a semester.
Students in year 8, 9 and 10 must select at least one science subject each year. Subjects are designed to help students to begin to specialise in their studies and prepare them for study at VCE level.
Note: A Year 10 student cannot undertake VCE Chemistry or Physics without teacher recommendation.